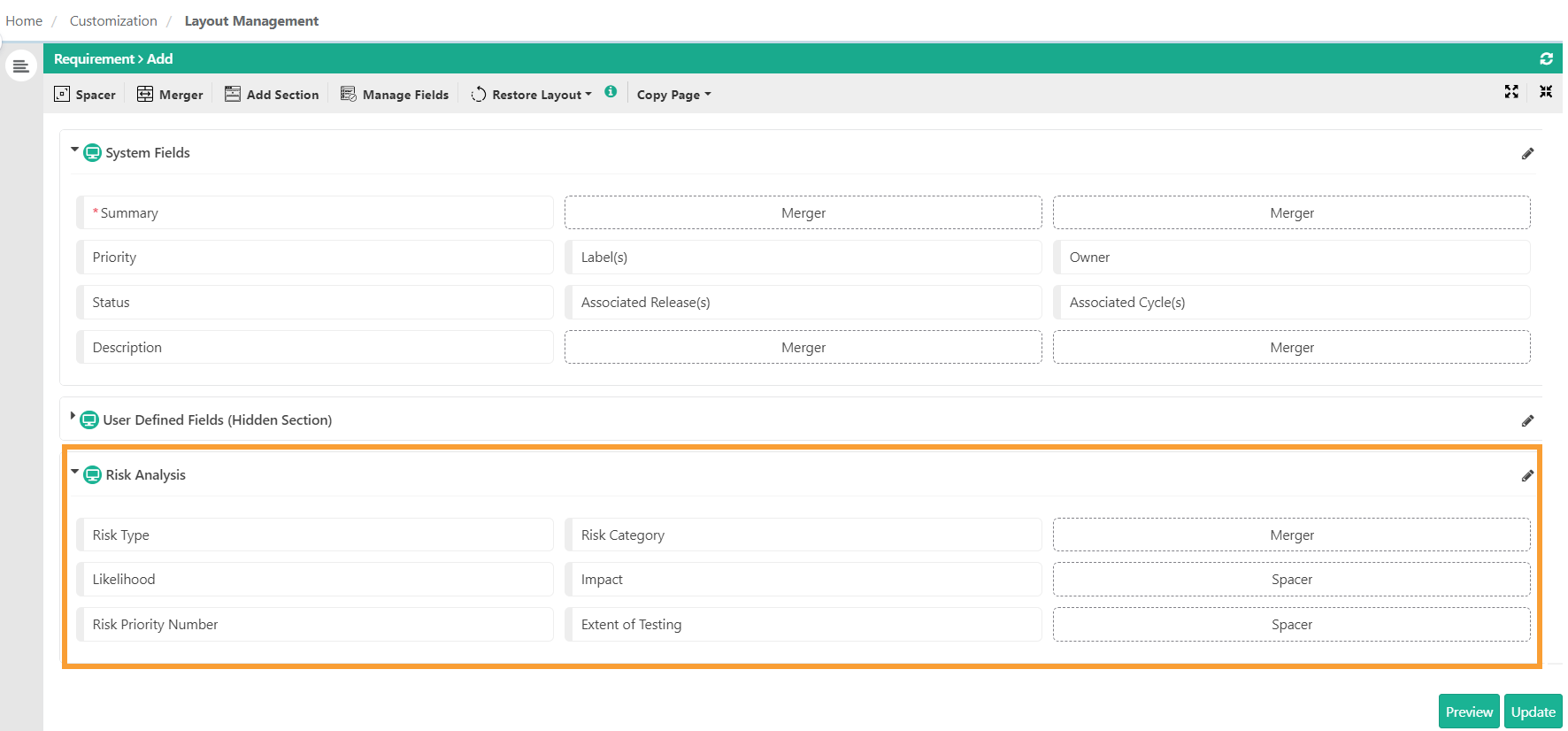
Accessing Risk-Based Testing Fields
Manage Fields
When RBT is enabled, the system auto-creates four new fields under Manage Fields under Customization. You can set them as mandatory, and add, archive, delete, or customize their values as needed.
Risk Type
Risk Category
Likelihood
Impact
Manage Lists
When RBT is enabled, the system automatically creates the following lists. You can edit existing values and add new ones.
Risk Likelihood
Value
Description
Value
Description
1
Least
3.5
Between High and Medium
1.5
Between Low and Least
4
High
2
Low
4.5
Between Very High and High
2.5
Between Medium and Low
5
Very High
3
Medium
Risk Impact
Value
Description
Value
Description
1
Least
3.5
Between High and Medium
1.5
Between Low and Least
4
High
2
Low
4.5
Between Very High and High
2.5
Between Medium and Low
5
Very High
3
Medium
Risk Type: The list is created with the values Project, Product, Process, and None.
Extent of Testing
E. T. Range (RPN Value)
Accepted format
>{Number}-{Number}Value
E. T. Range (RPN Value)
Accepted format
>{Number}-{Number}Value
>0 - 5
Report bugs only
> 20 - 25
Extensive
> 5 - 10
Opportunity
Out of Range
Not defined
>10 - 15
Cursory
> 15 - 20
Broad
Risk Category
Risk Category
Description
Competitive Inferiority
Failures to match competing systems in quality.
Data Quality
Failures in processing, storing, or retrieving data.
Date and Time Handling
Failures in date-based and/or time-based inputs/outputs, calculations, and event handling.
Disaster Handling and Recovery
Failure to degrade gracefully in the face of catastrophic incidents and/or failure to recover properly from such incidents.
Error Handling and Recovery
Failures due to bad inputs, beyond peak, or other illegal conditions (i.e., knock-on effects of deliberately inflicted errors).
Functionality
Failures that cause specific features not to work.
Installation, Setup, Upgrade, and Migration
Failures that prevent or impede deploying the system, and migrating data to new versions, including unwanted side-effects (e.g., installing additional, unwelcome, unintended software such as spyware, malware, etc.).
Interoperability
Failures occur when major components, subsystems, or related systems interact.
Load, Capacity, and Volume
Failures in scaling of system to the expected peak concurrent usage levels.
Localization
Failures in specific localities, including languages, messages, taxes and finances, operational issues, and time zones
Networked and Distributed
Failure to handle networked/distributed operation, including latency, delays, lost packets or connectivity, and unavailable resources.
Operations and Maintenance
Failures that endanger continuing operation, including backup or restore processes.
Packaging/Fulfillment
Failures associated with the packaging and/or delivery of the system or product.
Performance
Failures to perform as required under expected loads.
Portability, Configuration, and Compatibility
Failures specific to different supported platforms, supported configurations, configuration problems, and/or cohabitation with other software/systems.
Reliability, Availability, and Stability
Failures to meet reasonable expectations of availability and mean-time-between-failure.
Security/Privacy
Failures to protect the system and secure data from fraudulent or malicious misuse.
Standards Compliance
Failure to conform to mandatory standards, company standards, and/or applicable voluntary standards.
States and Transactions
Failure to properly respond to sequences of events or particular transactions.
Usability
Failures arise from aspects of the system that make players or other users feel ineffective, inefficient, or dissatisfied while using the system.
User Interface
Failures where incorrect information is presented directly to users.
Requirement Module
The Risk Analysis section appears on the Create and Edit screens for requirements. It includes:
Risk Type: Select from Project, Product, Process, or None.
Risk Category: Categorize the risk.
Likelihood: Select from 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, 5 (1 being the least and 5 being very high).
Impact: Select from 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, 5. (1 being the least and 5 being very high).
Risk Priority Number (RPN): Auto-calculated as RPN = Likelihood x Impact.
Extent of Testing (ET): Auto-calculated based on RPN value.
Test Case Module
The Risk Analysis section on the test case creation and edit screens includes the following fields:

Risk Type: Select from Project, Product, Process, or None.
Risk Category: Categorize the risk.
Likelihood: Select from 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, 5 (1 being the least and 5 being very high).
Impact: Select from 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, 5. (1 being the least and 5 being very high).
Risk Priority Number (RPN): Auto-calculated as RPN = Likelihood x Impact.
Extent of Testing (ET): Auto-calculated based on RPN value.
Test Case Created from Requirement
When you create a test case from a requirement, the system auto-populates the Risk Analysis fields from that requirement.
Screens Displaying RBT Field Values
When enabled, the system displays Risk Analysis columns on the following screens. Filter the records based on RBT fields.
Requirements tab in Test Case Module.
Link Requirements inTest Case Module.
Test Case Bulk Operations
Test Case tab under Requirement Module.
Requirement Bulk Operations.
Test Case tab in Test Suite Module.
Requirement tab in Issues Module.
Link Requirements screen in Issues Module.
Layout Management: Customize the Risk Analysis fields for the Test Case and Requirement module.
Warning
You cannot move or hide these fields—they must remain in the Risk Analysis section.