Flaky Test Detection
Flaky Score is an AI-driven feature that evaluates the stability of test cases by analyzing their execution history. It indicates the likelihood of a test case behaving unpredictably.
Flaky test cases can disrupt testing pipelines and undermine confidence in test results. Traditionally, identifying such tests required manual comparison of execution results across multiple runs. With flaky score, this process is automated.
QA Managers can define and configure settings according to their specific testing processes for calculating the flaky score, ensuring its relevance to their testing methodologies.
For example, the following table shows the execution results of the test cases executed multiple times.
Note
The system calculates the Flaky Score only for the executed test cases. It is determined based on the latest X number of executions. The Flaky Score ranges between 0 (Not Flaky) and 1 (Flaky).
Test Case Name | Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Test 4 | Test 5 | Test 6 | Test 7 | Test 8 | Flaky or Non-flaky? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Test Case A | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Pass | Non-flaky |
Test Case B | Fail | Fail | Fail | Fail | Fail | Fail | Fail | Fail | Non-flaky |
Test Case C | Pass | Pass | Fail | Fail | Pass | Fail | Pass | Fail | Flaky |
Note
The system considers only the final execution status assigned to the test case.
The system calculates Flaky Score only for the test executions of the same project.
Flaky Score Instance Level Settings
To activate the Flaky Score feature, the super administrator must enable it for the QMetry instance.
Go to Customizations.
Select General Settings and Audit and go to AI Configurations.
Scroll to the Flaky Score and Success Rate Configuration section.
Enable Allow Project Admins to Enable and Configure the Flaky Score for their project settings for Flaky Score calculations.
 |
Flaky Score Project Level Settings
To enable flaky score, you must enable these settings for individual projects in the QMetry instance.
Note
Ensure you have enabled Allow Project Admins to Enable and Configure the Flaky Score for their project in the Customization module.
Project admins and users with the Flaky Score - Modify or Flaky Score - Generate permissions can configure these settings.
To enable project-level settings for flaky score, perform the following steps:
Go to QMetry Intelligence.
Select Flaky Score Settings.
Open the Configurations tab.
Turn on Enable Flaky Score for the Project.
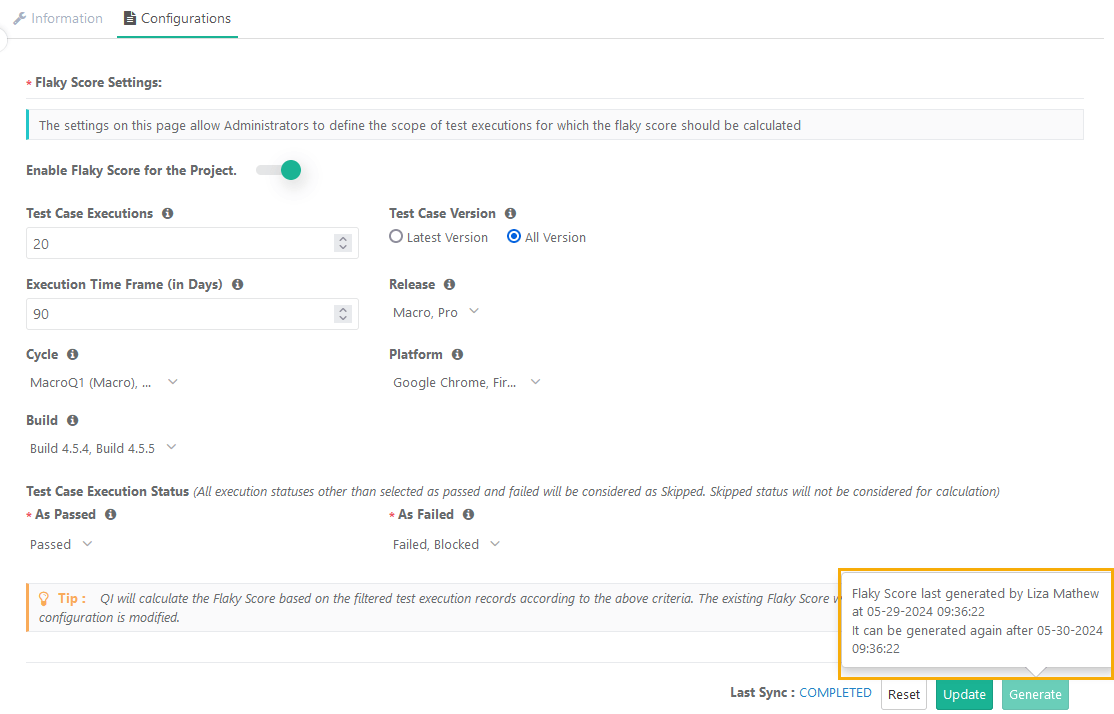
Flaky Score Configuration
Admins must define the scope of test executions for Flaky Score calculation. AI calculates the Flaky Score based on the filtered test execution records, using the specified criteria. The existing Flaky Score resets and recalculated whenever you modify the configuration.
Provide the following details for the Flaky Score rate configuration:
Test Case Executions: Mention the number of the latest test executions for a test case to consider while calculating the flaky score.
Note
By default, the system selects 10 test executions.
The Test Case Execution value should be from 1 to 1000.
Test Case Versions: Select the executions for either the “Latest Version” or “All Version” test case versions to consider while calculating the flaky score. The “Latest Version” test case version is selected by default.
Latest Version: The system considers only the latest executions of the latest versions of the test cases.
All Versions: The system considers the latest test executions of all test case versions.
Execution Timeframe (days): Mention the days to define the timeframe in which the test executions were executed in the last specified days.
Note
By default, the system considers test executions from last 90 days.
If left blank, the system considers all days.
Release: Select Releases to consider test executions for those releases. By default, the system selects “All” releases.
Cycle: Select Cycles to consider test executions for those cycles. By default, the system selects “All” cycles.
Platform: Select Platforms to consider test executions for those platforms. By default, the system selects “All” platforms.
Build: Select builds to consider the test executions pertaining to that particular builds. By default, the system selects “All” builds.
Test Case Execution Status (The system considers all execution statuses other than as passed and failed as Skipped. The system do not consider skipped statuses for calculation).
As Passed: The system considers test executions with these statuses as "Passed". The default value is “Passed”.
As Failed: The system considers test executions with these statuses as "Failed". The default values are “Failed” and “Blocked”.
Click Update to save the Flaky Score Settings.
To reset the settings, click Reset.
To generate the flaky score, click Generate.
Note
By default, the system selects “All” platforms.
When you hover over the Generate button, it displays the details of the user who generated the Flaky Score most recently, along with the timestamp.
 |
Once you generate the Flaky Score on the Flaky Score Settings screen, you can view the Flaky Score on the test case list view, test case details screen, test case link screens, and test execution screens.
You can show or hide the Flaky Score column on the test case list view, test case details screen, test case link screen, and test execution screens.
Displaying Flaky Score
The lesser the value (closer to 0), the less flaky the test case. It means the behavior is deterministic.
The larger the value (closer to 1), the greater the flakiness of the test case. It means the behavior is non-deterministic.
The following table interprets the intensity of the flaky score in accordance with its derived calculation and color code.
Flaky Score Range | Intensity of Flakiness |
|---|---|
Between 0.81-1 | High |
Between 0.41-0.80 | Medium |
Between 0-0.40 | Low |
Filter Test Cases on Flaky Score
You can filter the test cases based on the Flaky Score. You can find the Flaky Score under the Advanced Filters.
View Flaky Score on Test Case List View
According to the Flaky Score settings configured in the Configuration, the Flaky Score is calculated and displayed on the test case list view. It allows QA managers and Testers to view the risk probability and test execution history.
Go to the Test Cases module and make the Flaky Score column visible for the list view.
Flaky Score: It is calculated based on the frequency of pass or fail results.
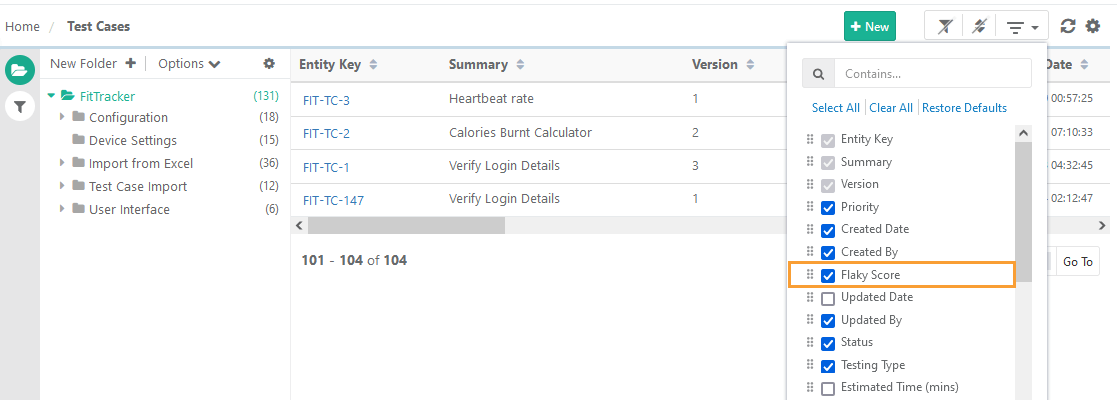
You can view the Flaky Score column, along with its corresponding statistics. You can sort on the column to view test cases with higher flaky scores.
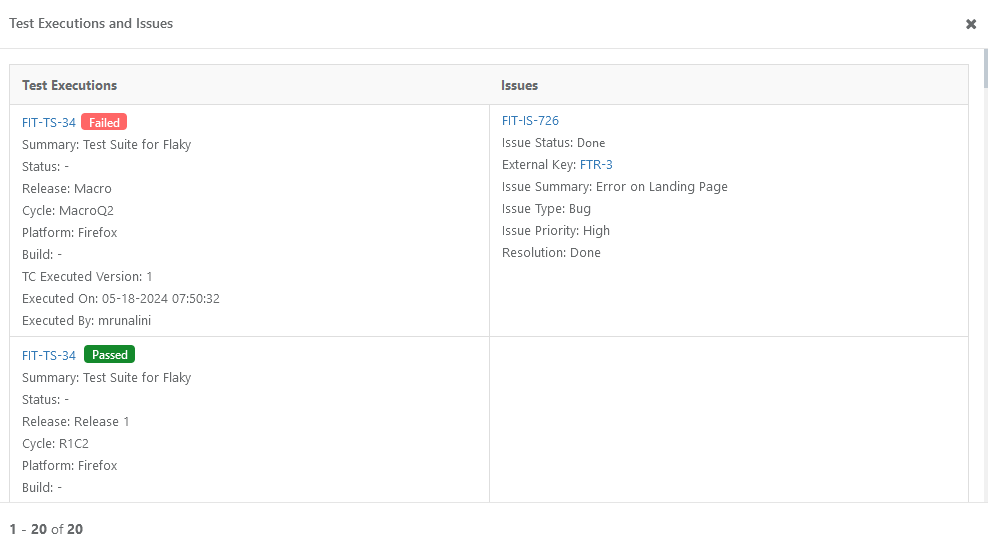
Click the Flaky Score to view the traceability report for the test case, which shows the test case is associated with which test executions, issues, and execution results. The report helps you further analyze the Flaky Score.
 |
If the Flaky Score Settings are changed, the existing Flaky Score will get reset.
The info icon beside the Flaky Score column displays the details of when the score was last generated and by whom.
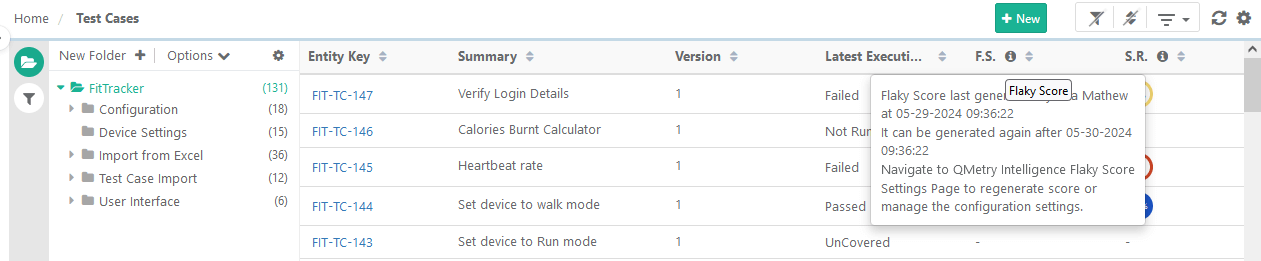 |
View Flaky Score on Test Case Detail Page
The generated Flaky Score is displayed beside the Test Case Key at the top of the screen.
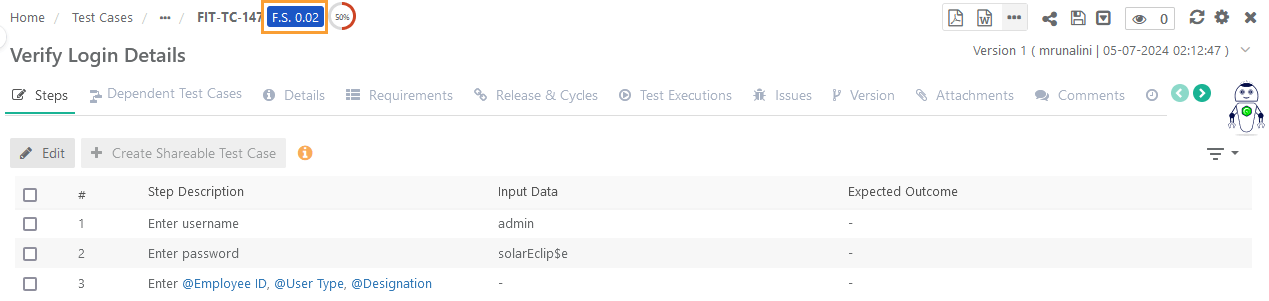 |
View Flaky Score on Test Case Link Screens
You can show or hide the Flaky Score column on the Link Test Cases screen.
View Flaky Score on Test Execution Screen
According to the Flaky Score settings configured in the Configuration, the system calculates the Flaky Score. The flaky score indicates the tester's probability of risk while executing the test case and provides a means for comparing pre- and post-test execution results.
Go to the Test Execution screen.
Test Execution Detail View
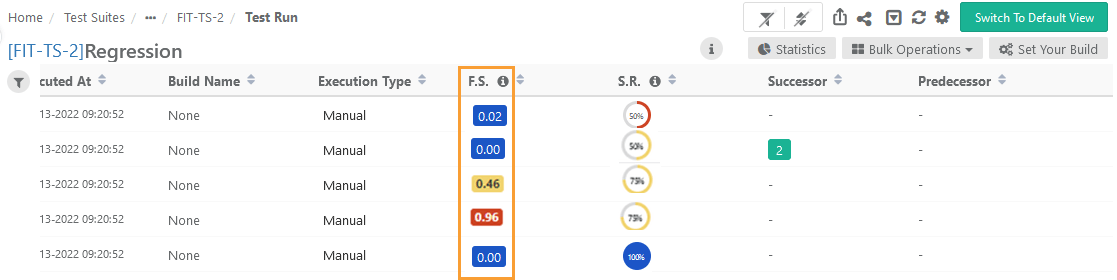 |
If you go further into the Detail View, you can view the Flaky Score count at the top of the page.
Test Execution Default View
You can show or hide the Flaky Score column on the execution screen.
Click the Flaky Score to drill down to view the test executions and defects associated with the test case.
How to Reduce Flakiness?
Flaky tests can occur due to various reasons. Testers should work with their development teams to find the exact reason for the cause. Here are the 10 common causes of flaky tests:
1. Async wait:
Some tests are written in a way that requires waiting for something else to complete. Many flaky tests use sleep statements for this purpose. However, sleep statements are imprecise, and the test may fail if the waiting time exceeds expectations due to variations in processing time.
2. Concurrency issues:
Flaky tests can result from concurrency issues such as data races, atomicity violations, or deadlocks. These tests often make incorrect assumptions about the ordering of operations performed by different threads. To address this, synchronization blocks can be added or the test can be modified to accommodate a wider range of behaviors.
3. Test order dependency:
Certain tests may pass or fail depending on the order in which preceding tests were executed. A good test should be independent and able to run in any order with other tests. It should be properly isolated and set up its own expected state.
4. Timing issues:
Flaky tests can arise from timing inconsistencies when the test code relies on specific event timings. For example, if a test checks for a particular webpage element after a specific delay, network issues or differences in CPU performance between test runs can lead to intermittent failures.
5. Element locator issues:
Many automation tools use XPath to locate webpage elements, but XPath can be unstable as it is sensitive to changes in the page's DOM. Self-healing AI techniques can address challenging testing scenarios involving dynamic elements, iFrames, and pop-ups. This involves using multiple locator strategies to find an element, and switching to a backup strategy if the primary one fails. Modifications to an element's properties or the addition of similar elements can render the initial XPath invalid, resulting in false positives or negatives.
6. Test code issues:
Poorly written or ambiguous test code can contribute to flaky tests. If the test code lacks clarity regarding the expected application behavior, the test may fail or pass inconsistently. Additionally, complex test code or code relying on external dependencies may be more prone to failure.
7. Test data issues:
Tests that depend on inconsistent test data can become flaky. Corrupted test data or different test runs using the same data can lead to inconsistent results. Tests utilizing random data generators without considering the full range of possible results can also introduce flakiness. It is advisable to control the seed for random data generation and carefully consider all possible values.
8. Test configuration issues:
Inconsistent test configurations between runs can cause flaky tests. Incorrect test parameters or improper test settings setup can result in test failures.
9. Environment issues:
Flaky tests can be attributed to the execution environment. Network connectivity problems, improper handling of I/O operations, hardware differences between test runs, or variations in test environments can introduce nondeterminism, leading to flaky tests.
10. Resource leaks: Tests can become flaky if the application or tests do not adequately acquire and release resources, such as memory or database connections. To avoid such issues, it is recommended to use resource pools and ensure that resources are properly returned to the pool when no longer needed.