Auto-Generate SQL with QI
The AI-powered, QI Query Assistant allows users to generate custom SQL reports directly from QMetry Insight using QMetry Intelligence (QI). The Query Assistant streamlines the reporting process, allowing users to create, modify, or comprehend SQL queries without requiring extensive SQL knowledge. The Query Assistant supports the following three use cases:
Generate a New Query - The QI Query generator creates SQL queries based on user-defined reporting needs expressed in simple English, aligned with the QMetry reports schema available in QMetry Insight.
Updating an Existing Query - The QI Query generator can help users modify existing SQL queries by adding fields and filters or implementing new logic and operators. To do this, users provide the existing SQL and clear instructions for the desired modifications in English. The output is an updated custom SQL query reflecting these changes.
Explaining Query - The Query Assistant empowers users to understand SQL queries by providing explanations of their logic, tables, and structure. This guidance enables users to comprehend the purpose and functionality of the query, aiding in debugging and troubleshooting.
Best Practices
All features operate according to the QMetry reports schema available in QMetry Insights. As a best practice, users must clearly describe their reporting needs in detail, specifying exact field names and any conditions or operations such as grouping, filtering, or sorting. The Query generator currently does not support user-defined fields and works only with system fields.
Permission, Configuration and Settings
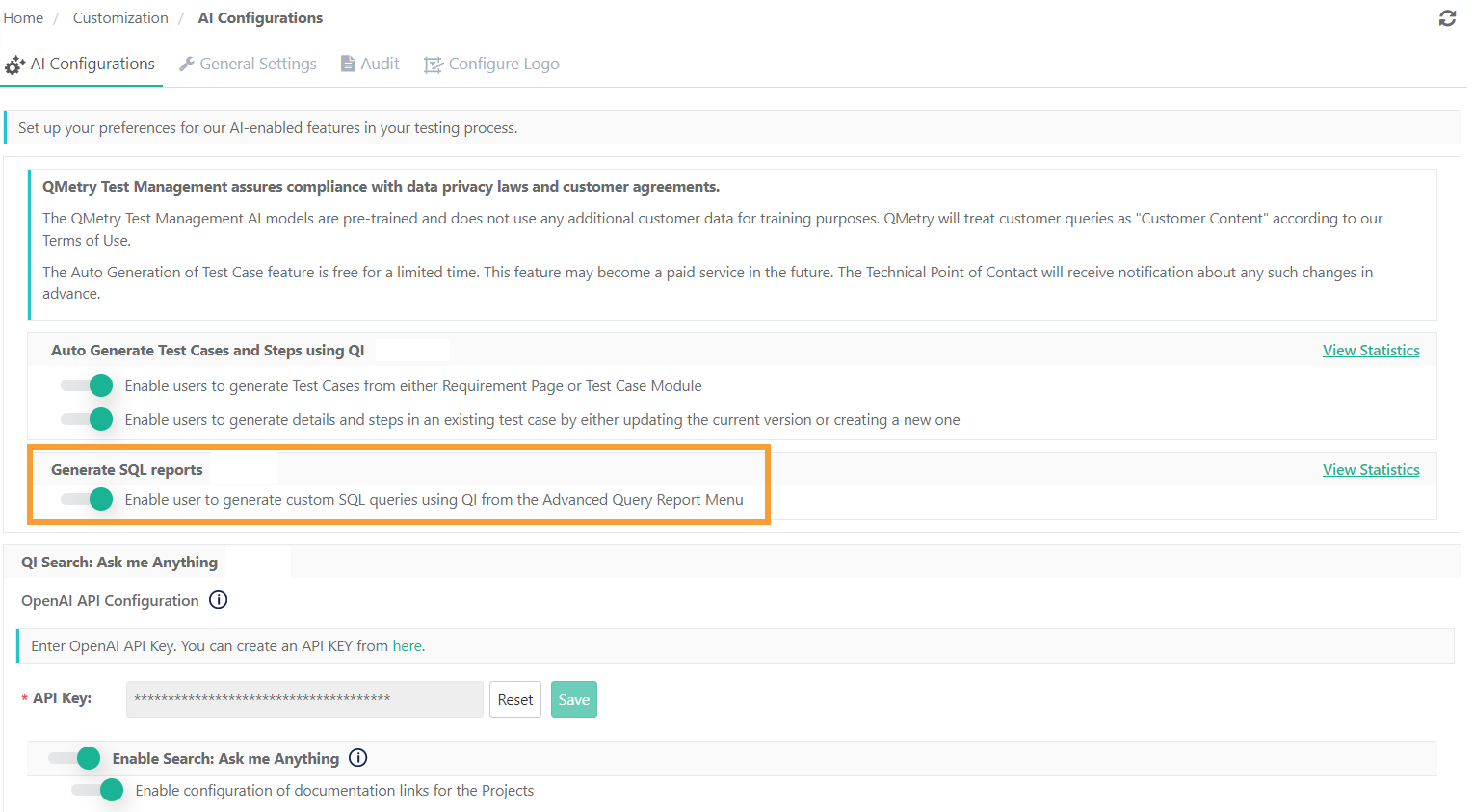
To activate QI auto-generated SQL queries, the QMetry super administrator must enable the setting at the instance level. They can do this from the AI Configuration tab within General Settings and Audit in the Customization module.
Permissions:
Only a super admin can access and configure QMetry Intelligence Configuration.
The default setting for the QI feature is disabled.
 |
Auto-Generate SQL with QI
Once the super admin enables the Generate SQL Reports toggle (as shown in the image above), users will see the Classic View and QI View buttons on the advanced query reports screen.
How it works
Upon activating the feature, users will see a new QI View under the Advanced Query Reports menu in QMetry Insights, alongside the existing Classic View. The QI View provides instructions and best practices for generating queries. Users can switch between the Classic SQL generation view and the QI View as needed.
Auto-Generate SQL with QI
To auto-generate SQL with QI, perform the following steps:
Go to the Advance Query Reports screen.
Click QI View to access the Generate SQL Using QI.
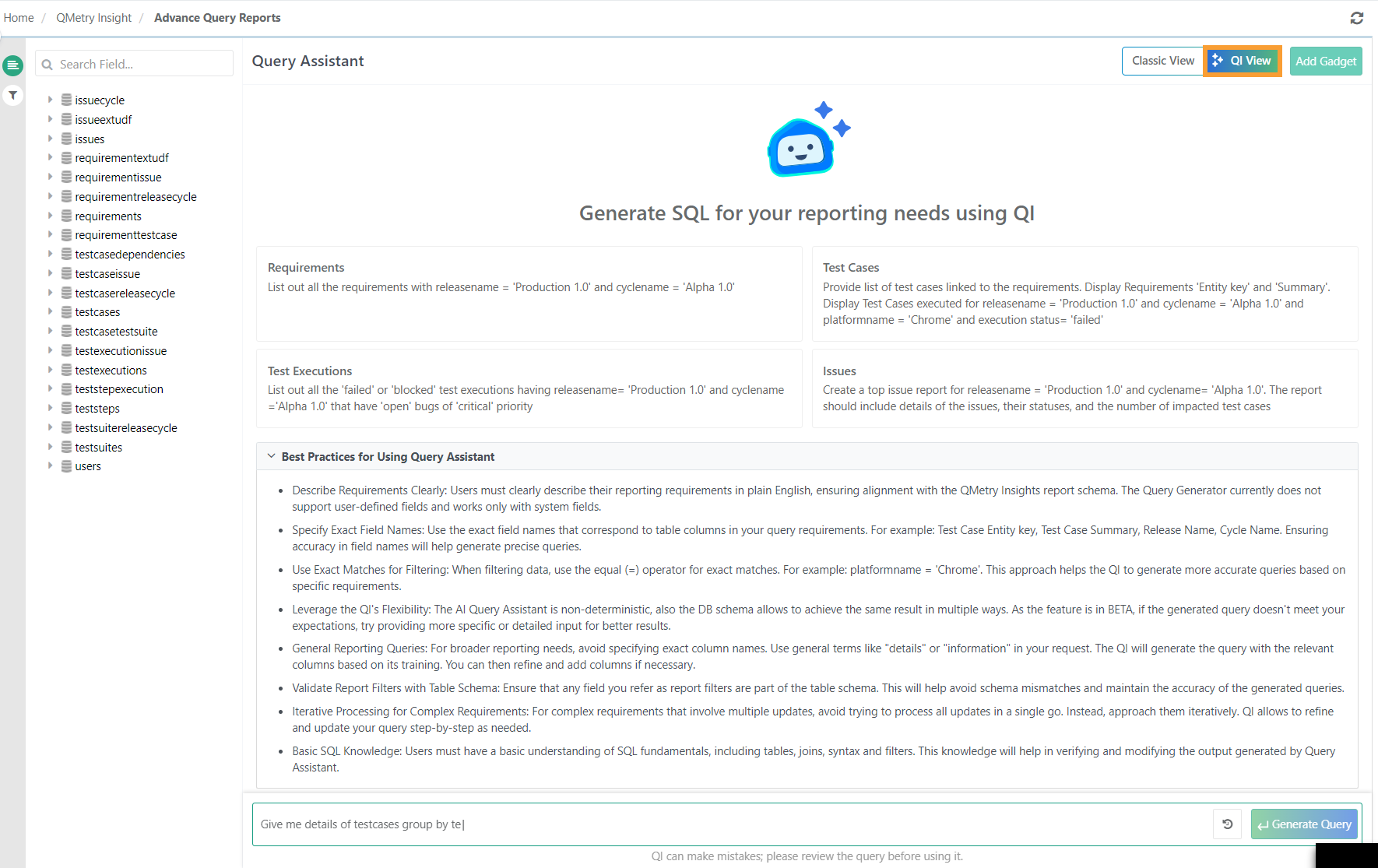
Provide a concise description of the reports you want to generate in plain English.
Add the needed filters as prompted. A list of predefined filters can be found in the Filters section on the left side of the screen.
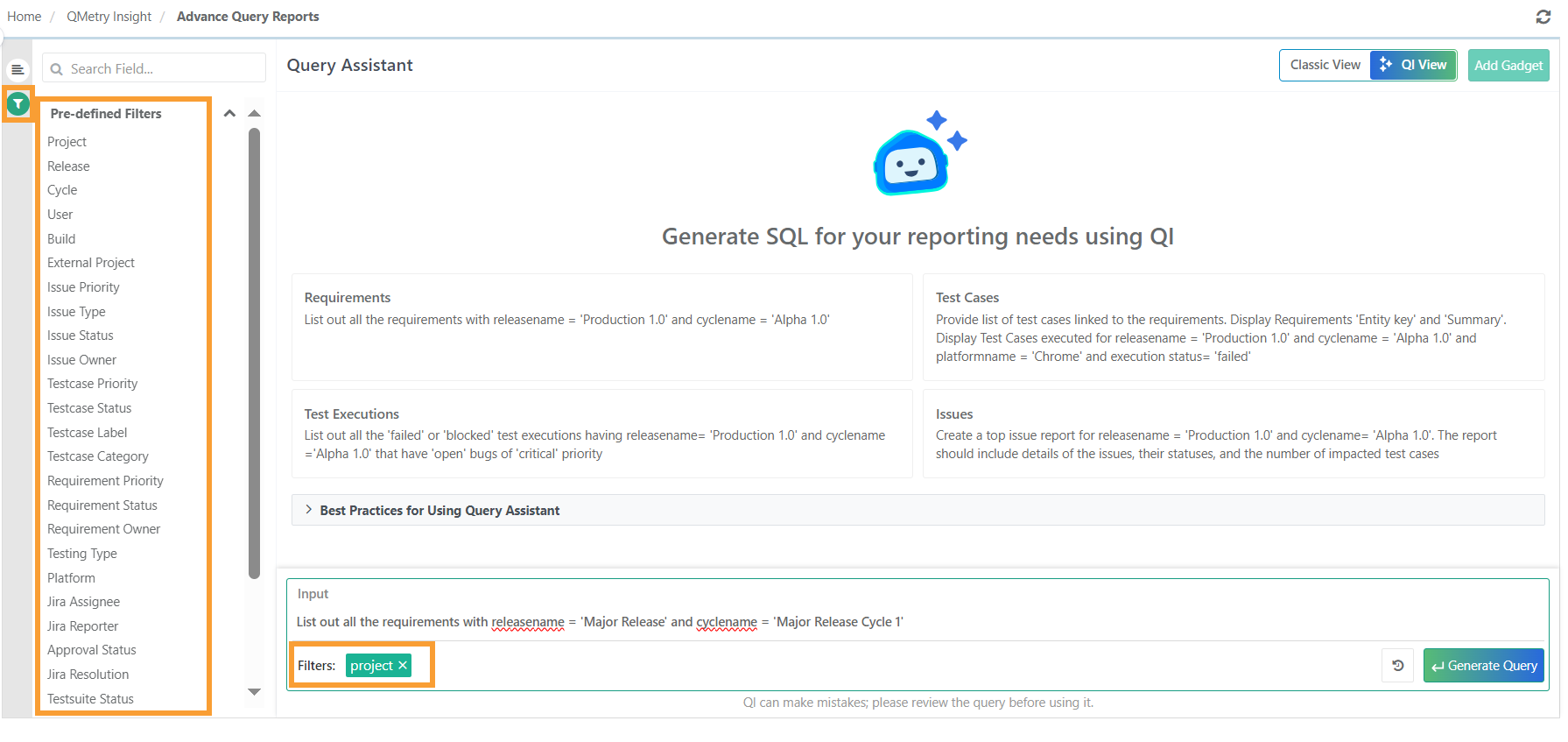
After adding the filters, click Generate Query.
Once the query is generated, click Fetch Filters and Verify to confirm.
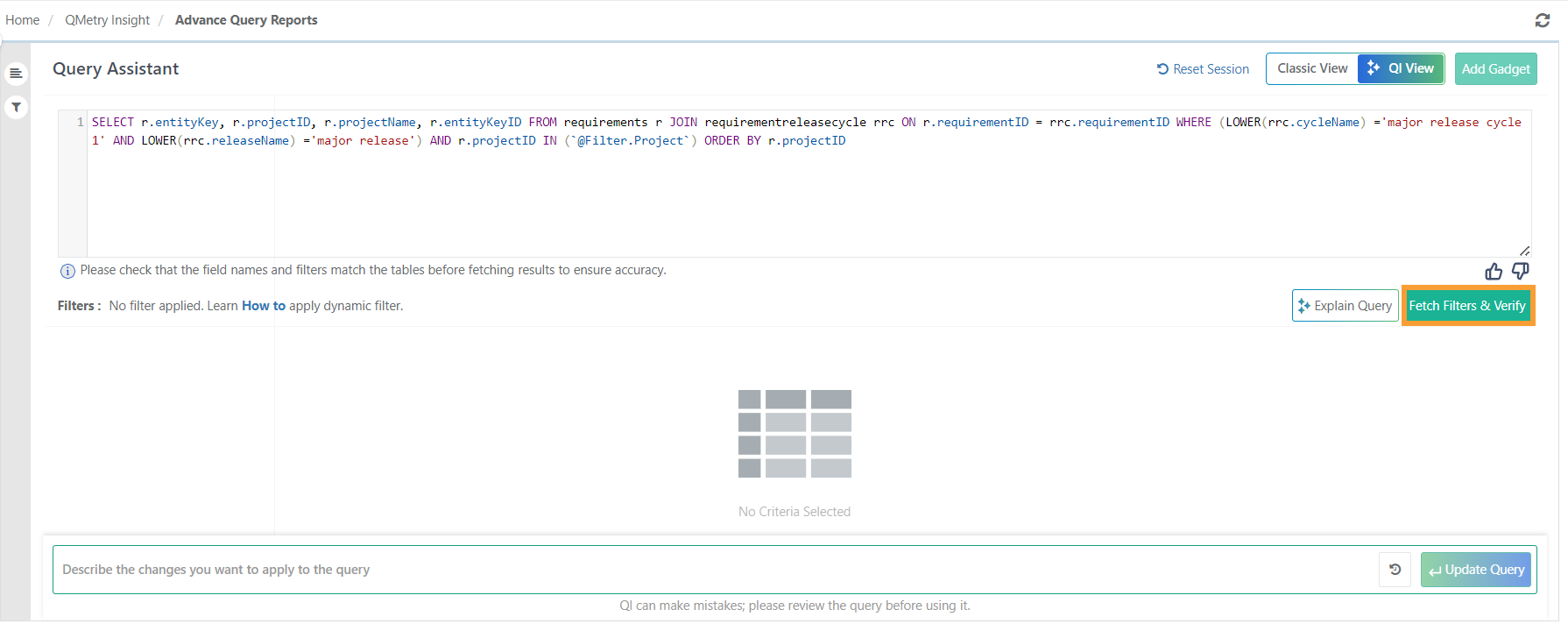
Select the appropriate project and click Run Query.
Review and validate the results.
Generic Prompts Examples
Simple Prompts
List all the requirements with the releasename
Production 1.0and cyclenameAlpha 1.0.Fetch all the requirements that are linked with test cases.
List out all the test cases with releasename =
Production 1.0and cyclename =Alpha 1.0.Fetch all the test cases that are linked with test suites.
Fetch all test executions with an
approvedstatus.List out all the
failedorblockedtest executions having releasename =Production 1.0and cyclename =Alpha 1.0that haveopenbugs ofcriticalpriority.Fetch all issues with a
blockerpriority andopenstatus.List all the Issues that are linked with test cases.
Fetch details like user alias and last login time for all the active users.
Complex Prompts
Need a report of testexecutions of releasename =
xyzand cyclename =abc. Also include issue details like status, the count of impacted test cases, and a list of the impacted test cases per issue for the test executions.Provide entity key and summary of defects found during the execution of test cases, categorized by their status, priority. Issues should have a requirement linked.
A report that shows the total count of executions executed grouped by execution status.
Generate a report having cumulative totals for executions executed daily and grouped by execution status.
Update QI Generated Query
Users can request further modifications and provide specific instructions for the desired changes to the query.
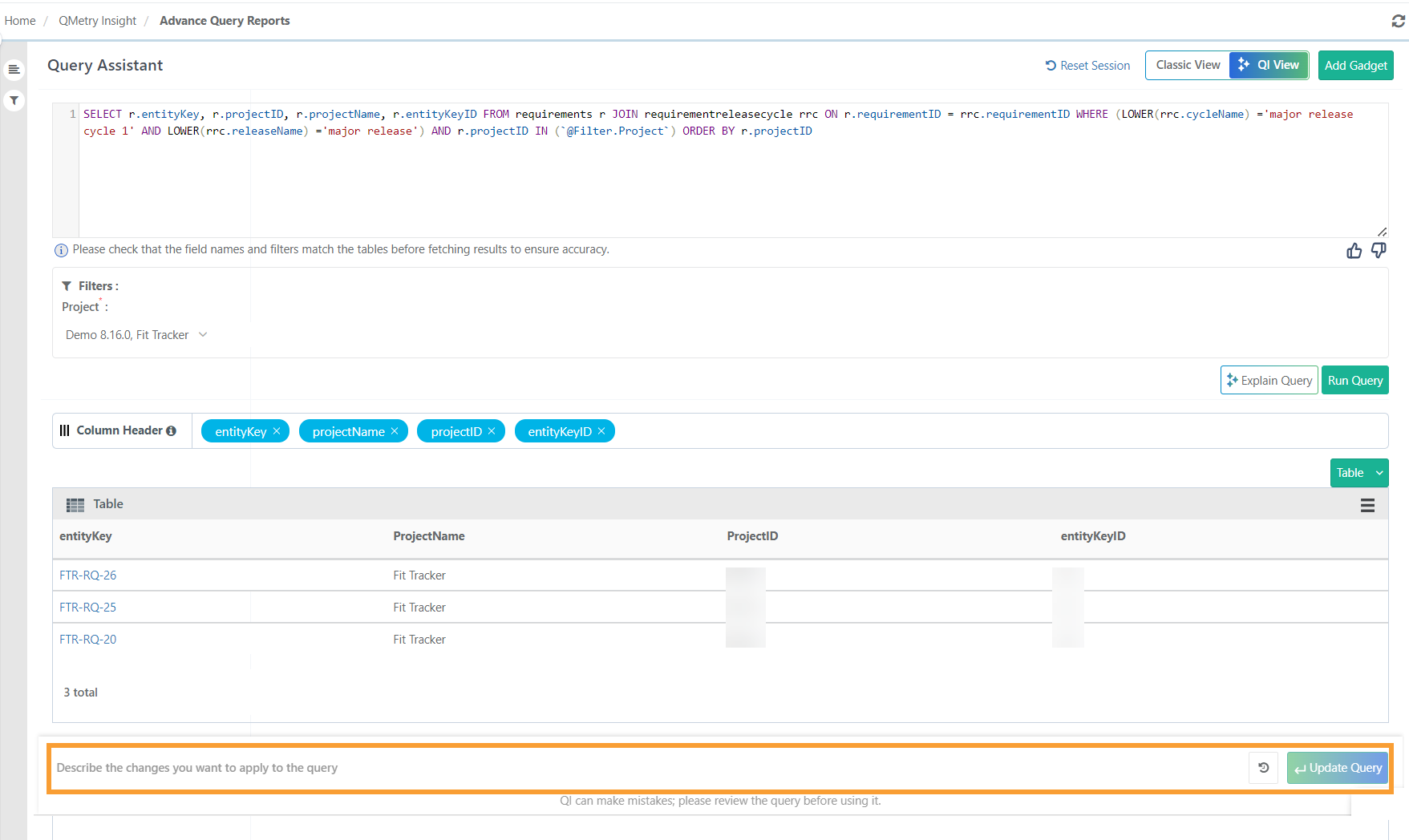 |
Examples:
Modify the query to showcase "Blocker" issues as "Blocker, Critical, and Medium."
Change a query displaying the Test Case Key and Summary to include Test Case Labels, Priority, and Status.
Update a query to show test cases linked to test executions having issue linked.
Add a filter for Execution Status and Platform alongside existing filters for Project, Release, and Cycle.
Group results by Execution Status or Platform.
Sort issues by created date in descending order.
Provide Feedback
To provide feedback on the QI-generated SQL query, click Thumbs Up or Thumbs Down. A pop-up appears with predefined options, allowing you to choose or submit custom feedback. This helps improve the model's accuracy and performance.
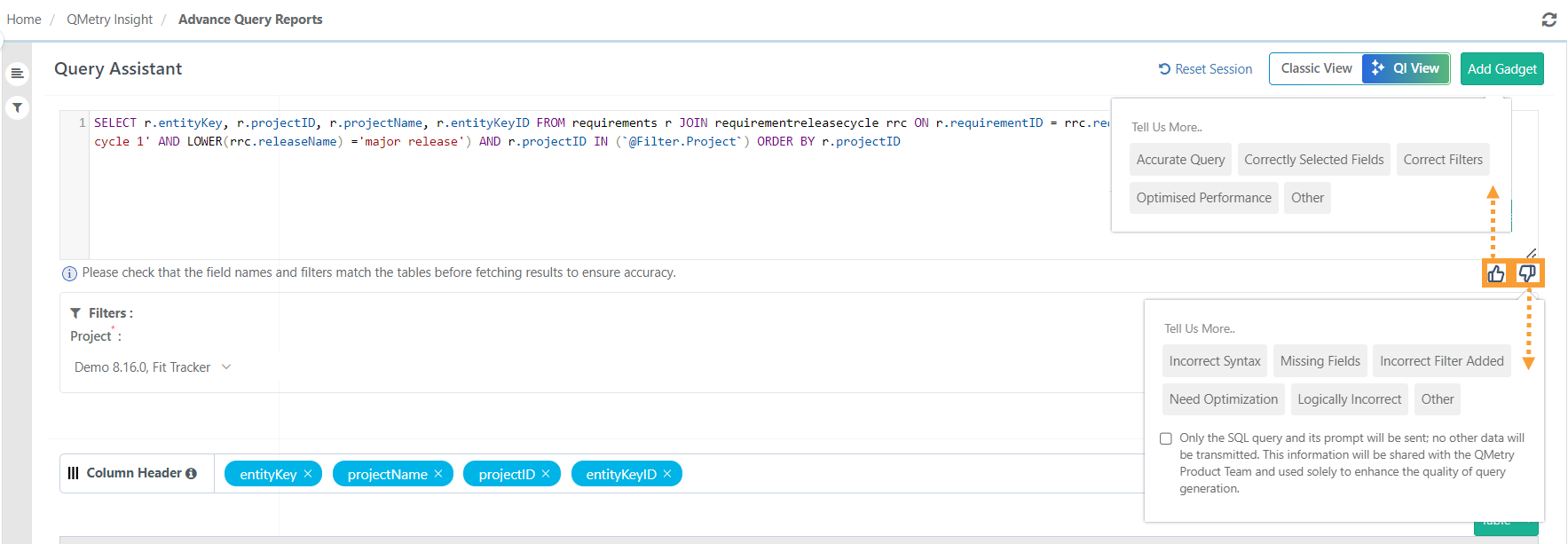 |
To submit feedback beyond the predefined options, select Other and enter your feedback in the pop-up that appears.
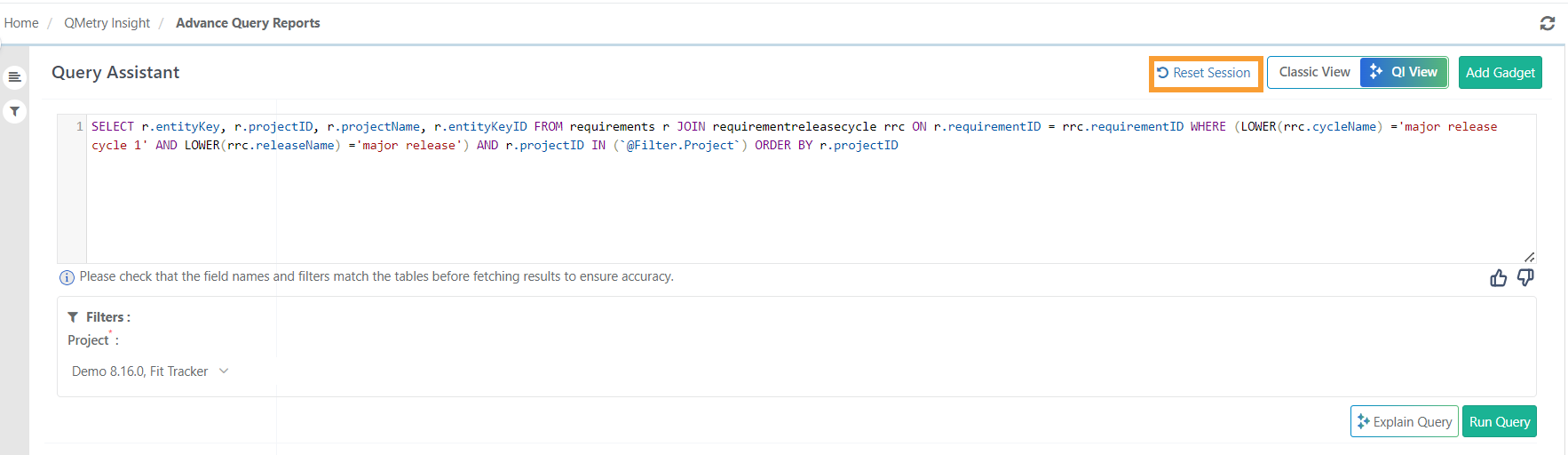
Reset session
You can reset the SQL query generation page by clicking the Reset Session button.
 |
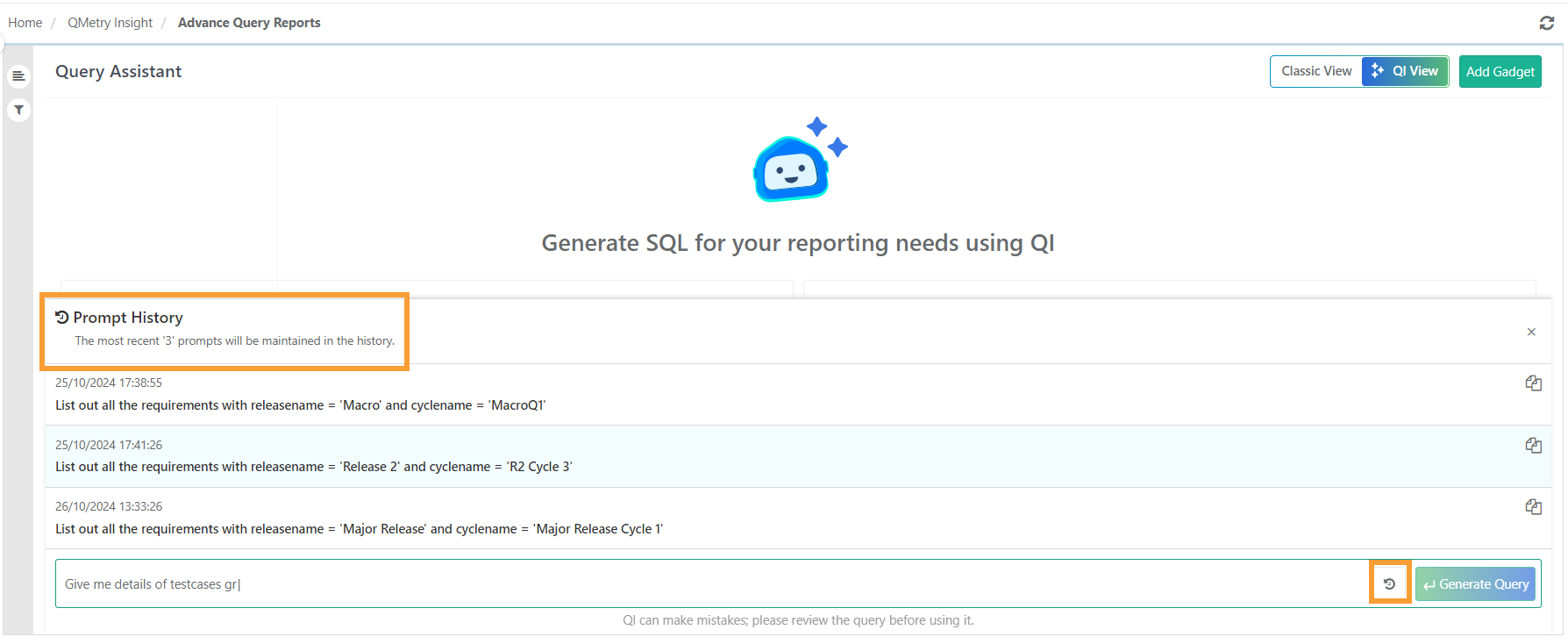
Prompt History
You can access the last three prompts for quick reference by clicking the Prompt History button.
 |
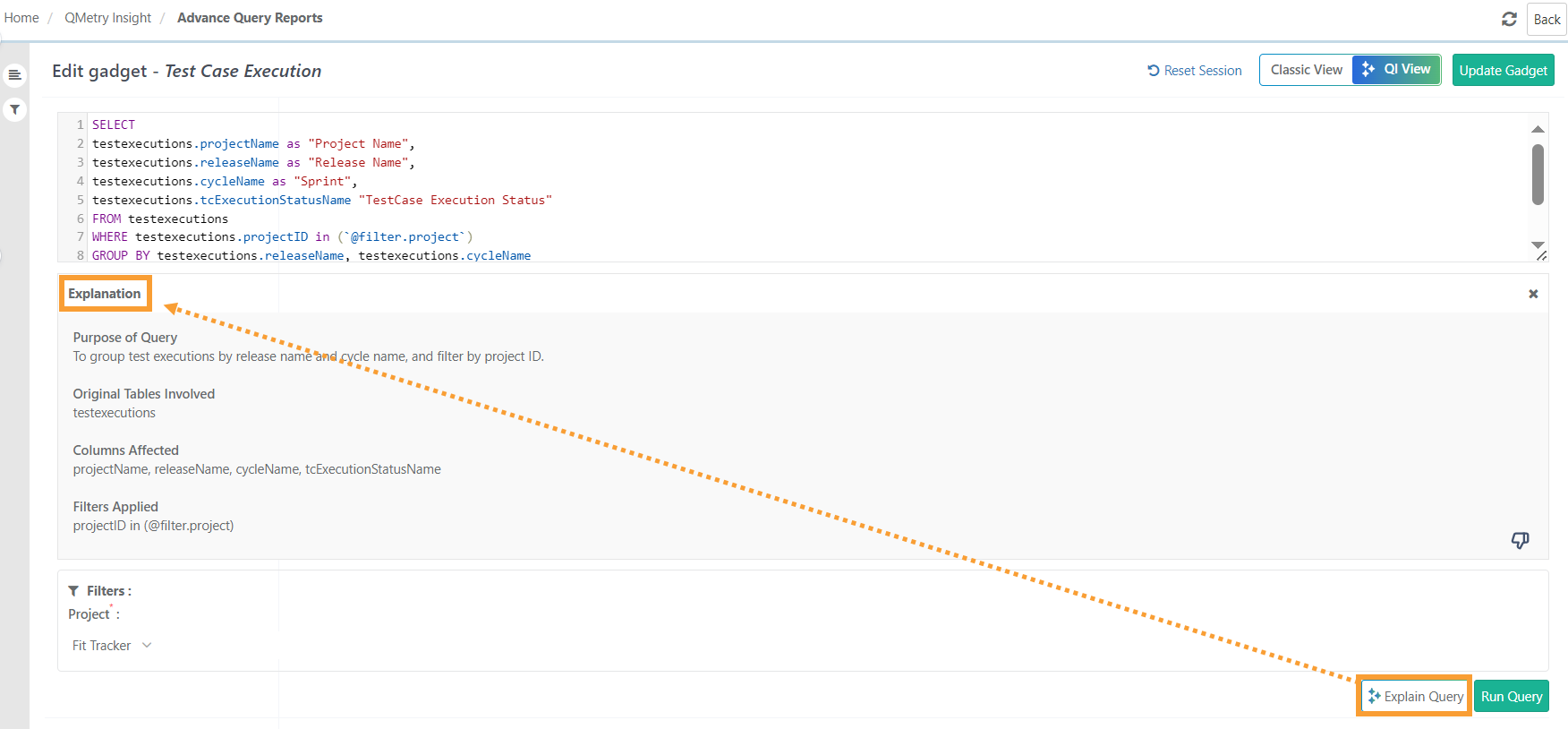
Explain Query
The QI Explain Query feature empowers users to understand SQL queries by providing explanations of their logic, tables, and structure. This guidance enables users to comprehend the purpose and functionality of the query, aiding in debugging and troubleshooting.
The Explain Query output includes:
Purpose of Query: A clear description of the query’s objective and functionality.
Original Tables Involved: A list of all tables referenced or used in the query.
Columns Affected: A list of all columns affected or used within the query.
Filters Applied: Details of any system filters included as part of the query logic.
 |
QI Statistics
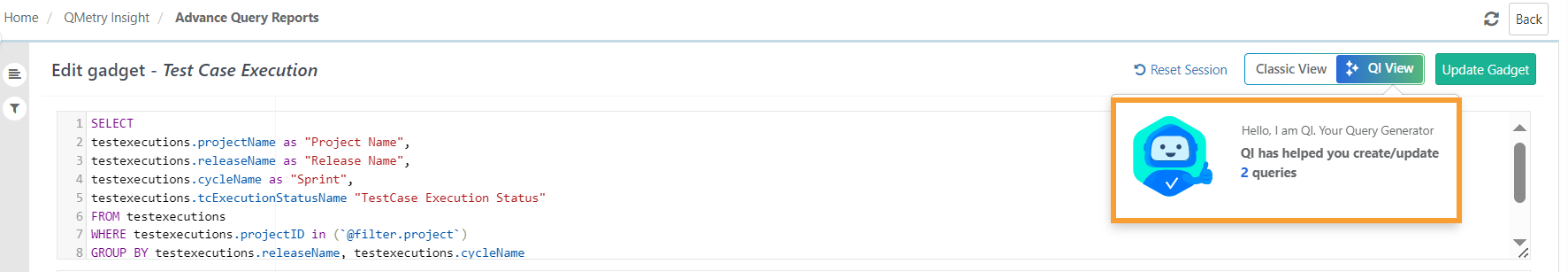
System administrators can monitor the usage of the SQL generator feature for all users.
Statistics for creating and updating reports using SQL queries generated by QI are accessible in General Settings > AI Configurations.
Users can hover over the QI Statistics button to view detailed information on the usage of the QI query generator.
 |
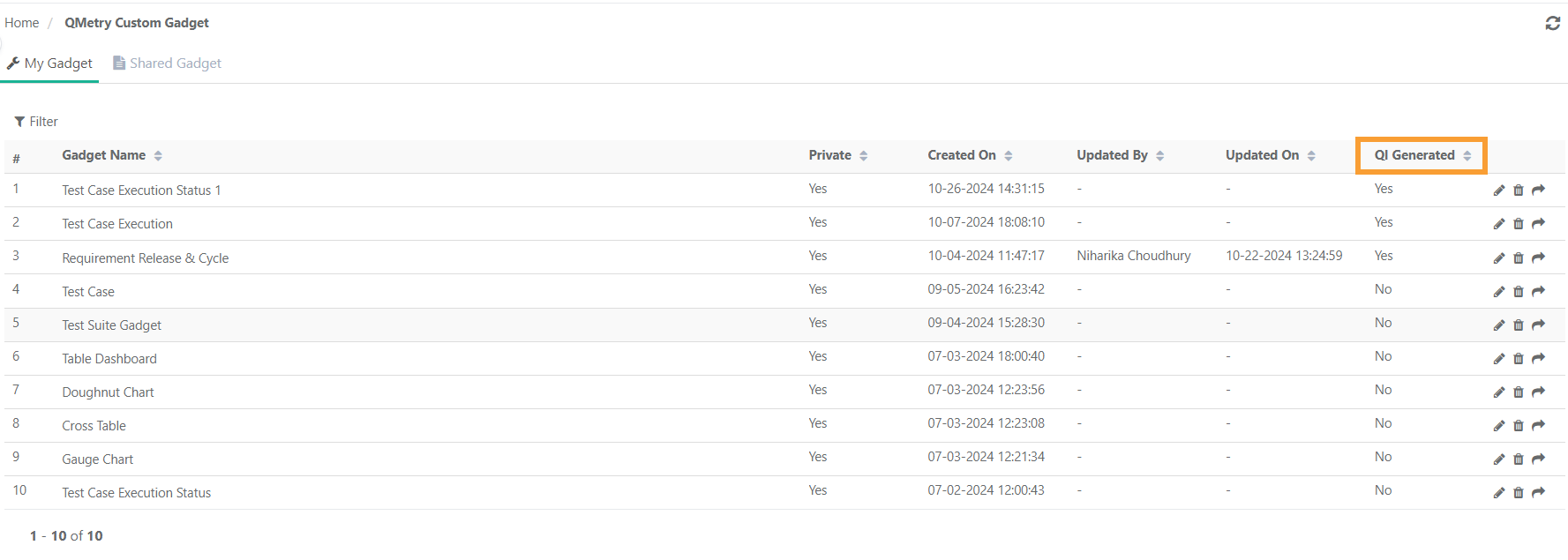
Identify QI-Generated Reports
Reports created using SQL queries generated using QI will display the QI logo when added to dashboards. The Custom Gadget list view includes a QI-generated column to identify reports generated with SQL queries from QI.
 |